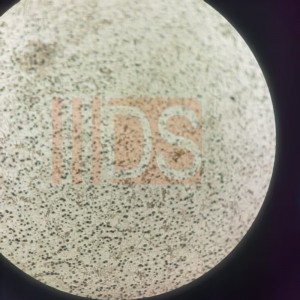
In modern industry, ductile iron pipes are widely used in water supply, drainage, gas transmission and many other fields due to their excellent performance. To deeply understand the performance of ductile iron pipes, the metallographic diagram of ductile iron pipes plays a vital role. Today, we will discuss the role of metallographic diagrams of ductile iron pipes in depth, and focus on analyzing the excellent value brought by DINSEN ductile iron pipes reaching level 1 spheroidization rate. The following figure is a photo of the metallographic diagram of DINSEN ductile iron pipes.

In simple terms, metallographic diagrams are images of the internal structure of metals observed by metallographic microscopes and other equipment after specific sample preparation of metal materials. For ductile iron pipes, their metallographic diagrams show key information such as the distribution state, shape characteristics and degree of spheroidization of ductile iron in the cast iron matrix. When preparing metallographic samples, a series of delicate operation processes such as cutting, grinding, polishing and corrosion are required. Cutting should ensure that the selected samples can represent the characteristics of the overall pipe; the grinding process gradually eliminates the surface damage caused by cutting, so that the surface flatness meets certain requirements; polishing further makes the sample surface smooth as a mirror, so that the internal structure can be clearly shown after subsequent corrosion treatment; corrosion is the use of chemical reagents to react with different metal structures to different degrees, so as to present clear differences in organizational structure under the microscope. Through this series of operations, we can obtain a metallographic diagram that can accurately reflect the microstructure of ductile iron pipes.
Material performance research: The performance of ductile iron pipes is closely related to the state of graphite nodules. From the metallographic diagram, we can intuitively see the size, number and distribution of graphite nodules. The size of graphite nodules directly affects the mechanical properties of cast iron. Small and evenly distributed graphite nodules can effectively improve the strength and toughness of cast iron. For example, when the graphite nodules are small and evenly distributed, they can disperse stress more evenly and reduce stress concentration when subjected to external forces, so that ductile iron pipes have better compression and tensile properties. The metallographic diagram is like a code book of material properties. By interpreting it, researchers can gain a deep understanding of the relationship between the internal structure and properties of the material, and provide a basis for the development of better quality ductile iron pipe materials.
Quality control: In the production process of ductile iron pipes, metallographic diagrams are an important means of quality control. Each batch of ductile iron pipes produced needs to be metallographically tested. By comparing the metallographic diagram with the standard atlas, it can be determined whether the product meets the quality standards. If the metallographic diagram shows that the spheroidization of graphite balls is poor, such as a large amount of flake graphite or too low spheroidization rate, the performance of the batch of products may not meet the expected requirements. For manufacturers, timely detection of such quality problems can prevent unqualified products from entering the market and reduce economic losses. It also helps to improve production processes and improve product quality stability.
Failure analysis: When ductile iron pipes fail or fail during use, metallographic diagrams can provide key clues to find out the cause of the failure. For example, if a pipeline ruptures, by analyzing the metallographic diagram near the ruptured part, it may be found that the spheroidization rate of the graphite nodules decreases, resulting in reduced material toughness and brittle fracture under long-term external force; or because of impurities or defects in the structure, corrosion is caused under specific conditions, which eventually leads to pipeline failure. After the failure cause is clarified through metallographic analysis, targeted improvement measures can be taken, such as optimizing the production process, adjusting the raw material formula, etc., to improve the service life and reliability of ductile iron pipes.
Spheroidization rate is an important indicator for measuring the quality of ductile iron pipes. It indicates the degree of graphite spheroidization. The higher the spheroidization rate, the closer the shape of the graphite nodules is to a perfect sphere and the more uniform the distribution is. According to relevant standards, the spheroidization rate is usually divided into different levels, generally from level 1 to level 6, with level 1 having the highest spheroidization rate and level 6 having the lowest spheroidization rate.
Level 1 spheroidization rate: For ductile iron pipes that reach level 1 spheroidization rate, the graphite nodules inside are almost all perfectly spherical, uniform in size, and highly dispersed and evenly distributed. This ideal microstructure gives ductile iron pipes excellent mechanical properties. In terms of strength, it can withstand higher pressures, and can maintain a stable structure whether it is deeply buried in the ground to withstand soil pressure or when conveying high-pressure fluids. In terms of toughness, ductile iron pipes with a spheroidization rate of 1 have excellent impact resistance. Even under complex geological conditions, such as earthquake-prone areas, they can effectively resist the impact of factors such as ground displacement, greatly reducing the risk of pipeline rupture. At the same time, a good spheroidization rate also helps to improve the corrosion resistance of the pipe, because the uniform distribution of graphite balls reduces the electrochemical corrosion caused by microstructural differences.
The impact of different levels of spheroidization rate on performance: As the spheroidization rate decreases, the shape of the graphite balls gradually deviates from the spherical shape, and more elliptical, worm-like and even flake graphite appears. These irregularly shaped graphites will form stress concentration points inside the material, reducing the strength and toughness of the material. For example, the graphite balls of ductile iron pipes with a spheroidization rate of 3 are not as regular as those of level 1, and the distribution is relatively uneven. When subjected to the same pressure, they are more likely to be locally deformed or even ruptured. In terms of corrosion resistance, pipes with lower spheroidization rates are more susceptible to electrochemical corrosion due to the uneven microstructure, thus shortening the service life of the pipe.
Excellent mechanical properties: DINSEN ductile iron pipes have extremely high strength and toughness due to their grade 1 spheroidization rate. In water supply projects, they can withstand high water pressure, ensure stable water supply, and reduce the occurrence of pipe burst accidents. In drainage systems, facing the instantaneous high-flow drainage needs in extreme weather such as heavy rain, their high strength and good toughness can ensure that the pipeline is not damaged by water flow impact. In the field of gas transmission, the transmission of high-pressure gas requires extremely high pipeline strength. The grade 1 spheroidization rate of DINSEN ductile iron pipes makes it fully capable of this task, ensuring safe and reliable gas transmission.
Long service life: The uniform microstructure brought by the grade 1 spheroidization rate greatly improves the corrosion resistance of DINSEN ductile iron pipes. Whether in a humid underground environment or in an industrial wastewater discharge scenario containing corrosive media, its corrosion resistance is far superior to pipes with lower spheroidization rates. This means that during the use of DINSEN ductile iron pipes, the wall thickness of the pipe decreases slowly, and it can maintain good performance for a long time, greatly extending the service life of the pipe and reducing replacement and maintenance costs.
Wide application adaptability: Due to its excellent performance, DINSEN ductile iron pipes can adapt to various complex engineering environments and application requirements. Whether in the cold northern regions, it copes with the pressure caused by the expansion of water freezing in the pipe in winter, or in the hot and rainy southern regions, it resists corrosion in humid environments. It performs well in the fields of urban infrastructure construction, industrial engineering and agricultural irrigation, and provides reliable pipeline solutions for the development of different industries.
In summary, the metallographic diagram of ductile iron pipes plays an irreplaceable role in material research, quality control and failure analysis. The spheroidization rate level, especially the 1st level spheroidization rate achieved by DINSEN ductile iron pipes, is of decisive significance for improving the performance of ductile iron pipes, extending their service life and meeting a wide range of application needs. Through in-depth understanding of metallographic phase diagrams and spheroidization rate, we can better understand ductile iron pipes, an important industrial material, and give full play to their advantages in practical applications.
Post time: Mar-21-2025